Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 56:28 — 129.2MB)
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
Note: This episode is Part 2 of 2. It stands alone, but to start at Part 1 click HERE.
“So which strategy in this model is best? Every behavioral strategy is the right strategy for some problem, but no strategy is the best strategy for every problem. We need them all.”
– Dr Patricia Crittenden, creator of the Dynamic Maturational Model of Attachment & Adaptation (DMM) using culture and context.
LOOKING FOR THE SLIDES?
DOWNLOAD THE PDF HERE: Rudiments-of-the-DMM-PDF VERSION
OR THE POWERPOINT VERSION HERE: Rudiments of the DMM Powerpoint version
Or if you have great eyesight 🙂 you can view them here.


Therapist Uncensored Episode 97 Show Notes:
Before we begin:
- A’s (Red in the DMM)=Historically referred to as Blue on TU
- B’s (Blue in the DMM)=Historically referred to as Green on TU
- C’s (Green in the DMM)=Historically referred to as Red on TU
- AC’s = Historically referred to Tie Dye on TU
**Note: We know the colors may be a bit confusing, but it is important to us that you receive information as Dr Crittenden has published it. It is by happenstance that our colors are the same (with the exception of tie dye), but they represent different thinking and behavioral patterns. When we refer to color in the episodes and in the show notes, we are referring to the colors we have historically used on the TU podcast and the letters and self-protective strategies of the DMM. This is only in order to maintain consistency and make the information more easily understood by our listeners. However, the colors as shown in the slides and as listed above, are the way Dr Crittenden uses them in her fantastic work!
Let’s Dive In:
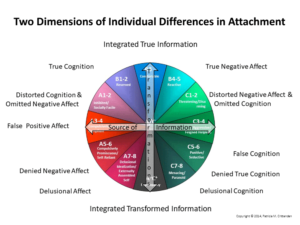
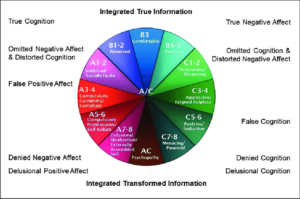
To understand self-protective strategies, we have to understand the information the brain is using, even in infancy – it’s neurological.
A’s, the B’s and the C’s emphasize different sorts of information.
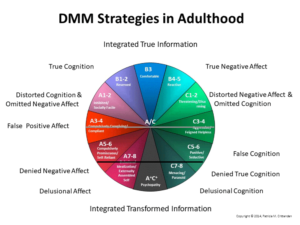
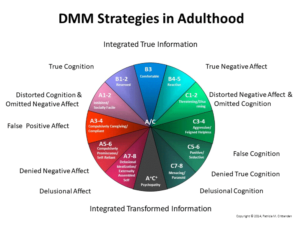
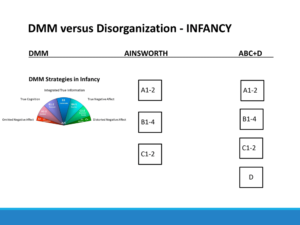
Strategies by Age Group and Model Representation:
Infancy
DMM Ainsworth ABC+D
A-2: Avoidant A1-2 A1-2
B1-2: Reserved B1-4 B1-4
B3: Comfortable C1 C1-2
B4-5: Reactive D-Controlling
C1-2: Resistant/Passive
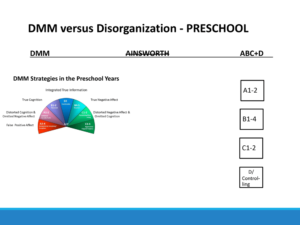
Preschool
- Preschoolers utilize false positive affect.
- A’s split their own self from the other, and they focus on the parent. They take the perspective of the powerful person.
- C’s split their negative affect, showing either the vulnerable or the invulnerable affect. They hide the other from view.
DMM Ainsworth ABC+D
A1-2: Avoidant A1-2
A3-4: Compulsively Caregiving/Compliant B1-4
B1-2: Reserved C1-2
B3: Comfortable D-Controlling
B4-5: Reactive
C1-2: Resistant/Passive
C3-4: Aggressive/Feigned Helpless
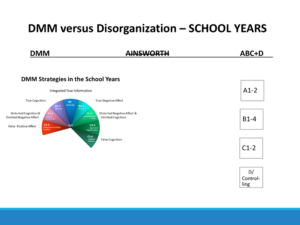
School Age
DMM Ainsworth ABC+D
A1-2: Avoidant A1-2
A3-4: Compulsively Caregiving/Compliant B1-4
B1-2: Reserved C1-2
B3: Comfortable D-Controlling
B4-5: Reactive
C1-2: Resistant/Passive
C3-4: Aggressive/Feigned Helpless
C5-6: Punitive/Seductive
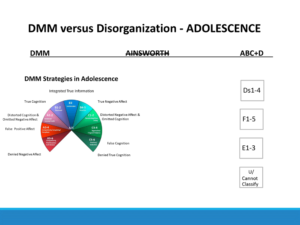
Adolescence
DMM Ainsworth ABC+D
A1-2: Avoidant A1-2
A3-4: Compulsively Caregiving/Compliant B1-4
A5-6: Compulsively Promiscuous/Self-Reliant C1-2
B1-2: Reserved U/Cannot Classify
B3: Comfortable
B4-5: Reactive
C1-2: Resistant/Passive
C3-4: Aggressive/Feigned Helpless
C5-6: Punitive/Seductive
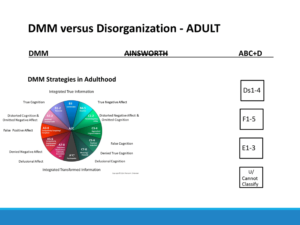
Adult
DMM Ainsworth ABC+D
A1-2: Avoidant A1-2
A3-4: Compulsively Caregiving/Comp B1-4
A5-6: Compulsively Promiscuous/Self-Reliant C1-2
A7-8: Delusional Idealization/Externally Assembled Self U/Cannot Classify
B1-2: Reserved
B3: Comfortable
B4-5: Reactive
C1-2: Resistant/Passive
C3-4: Aggressive/Feigned Helpless
C5-6: Punitive/Seductive
C7-8: Menacing/Paranoid
A/C: Includes Psycopathy (extreme A/C combination)
Description of each group:*
The A’s (our blue. red in the DMM)
A1-2: The A1-2 strategy uses cognitive prediction in the context of very little real threat. Attachment figures are idealized by over-looking their negative qualities (A1) or the self is put down a bit (A2). Most A1-2s are predictable, responsible people who are just cool and businesslike. Type A strategies all rely on inhibition of feelings and set danger at a psychological distance from the self. This strategy is first used in infancy.
A3: Individuals using the A3 strategy (compulsive caregiving, cf., Bowlby, 1973) rely on predictable contingencies, inhibit negative affect and protect themselves by protecting their attachment figure. In childhood, they try to cheer up or care for sad, withdrawn, and vulnerable attachment figures. In adulthood, they often find employment where they rescue or care for others, especially those who appear weak and needy. The precursors of A3 and A4 can be seen in infancy (using the DMM method for the Strange Situation), but the strategy only functions fully in the preschool years and thereafter.
A4: Compulsively compliant individuals (Crittenden & DiLalla, 1988) try to prevent danger, inhibit negative affect and protect themselves by doing what attachment figures want them to do, especially angry and threatening figures. They tend to be excessively vigilant, quick to anticipate and meet others’ wishes, and generally agitated and anxious. The anxiety, however, is ignored and downplayed by the individual and often appears as somatic symptoms that are brushed aside as being unimportant.
A5: A5 individuals use a compulsively promiscuous strategy (Crittenden, 1995) to avoid genuine intimacy while maintaining human contact and, in some cases, satisfying sexual desires. They show false positive affect, including sexual desire, to little known people, and protect themselves from rejection by engaging with many people superficially and not getting deeply involved with anyone. This strategy develops in adolescence when past intimate relationships have been treacherous, and strangers appear to offer the only hope of closeness and sexual satisfaction. It may be displayed in a socially promiscuous manner (that does not involve sexuality) or, in more serious cases, as sexual promiscuity.
A6: Individuals using a compulsively self-reliant strategy (Bowlby, 1980) do not trust others to be predictable in their demands, find themselves inadequate in meeting the demands or both. They inhibit negative affect and protect themselves by relying on no one other than themselves. This protects the self from others, but at the cost of lost assistance and comfort. Usually this strategy develops in adolescence after individuals have discovered that they cannot regulate the behavior of important, but dangerous or non-protective, caregivers. They withdraw from close relationships as soon as they are old enough to care for themselves. There is a social form of the strategy in which individuals function adaptively in social and work contexts, but are distant when intimacy is expected, and an isolated form in which individuals cannot manage any interpersonal relationship and withdraw as much as possible from others.
A7-8: Delusionally idealizing individuals (Crittenden, 2000) have had repeated experience with severe danger that they cannot predict or control, display brittle false positive affect, and protect themselves by imagining that their powerless or hostile attachment figures will protect them. This is a very desperate strategy of believing falsely in safety when no efforts are likely to reduce the danger (cf., the “hostage syndrome”). Paradoxically, the appearance is rather generally pleasing, giving little hint of the fear and trauma that lie behind the nice exterior until circumstances produce a break in functioning. This pattern only develops in adulthood.
Individuals using an A8 strategy (externally assembled self, Crittenden, 2000) do as others require, have few genuine feelings of their own, and try to protect themselves by absolute reliance on others, usually professionals who replace their absent or endangering attachment figures. Both A7 and A8 are associated with pervasive and sadistic early abuse and neglect.
The B’s (our green, blue in the DMM)
B1-2: Individuals assigned to B1-2 are a bit more inhibited with regard to negative affect than B3s but are inherently balanced.
B3: The Type B strategy involves a balanced integration of temporal prediction with affect. Type B individuals show all kinds of behavior but are alike in being able to adapt to a wide variety of situations in ways that are self-protective, that protect their children, and that as often as possible cause others no harm. They communicate directly, negotiate differences, and find mutually satisfactory compromises. They distort cognitive and affective information very little, especially not to themselves.
Finally, they display a wider range of individual variation than people using other strategies – who must constrain their functioning to employ their strategy. This strategy functions in infancy. By adulthood, two sorts of Type B strategies can be differentiated. Naive B’s simply had the good fortune to grow up in safety and security. Mature B’s, on the other hand, 1) have reached neurological maturity (in the mid-30’s), 2) function in life’s major roles, e.g., child, spouse, parent, and 3) carry out an on-going process of psychological integration across relationships, roles, and contexts. Where naive B’s tend to be simplistic, mature B’s grapple with life’s complexities.
B4-5: Individuals assigned to B4-5 exaggerate negative affect a bit, being sentimental (B4) or irritated (B5) but are inherently balanced.
The C’s (our red, blue in the DMM)
C1-2: The C1-2 (threatening-disarming) strategy involves both relying on one’s own feelings to guide behavior and using somewhat exaggerated/changing displayed negative affect to influence other people’s behavior. Specifically, the strategy consists of splitting, exaggerating, and alternating the display of mixed negative feelings to attract attention and manipulate the feelings and responses of others. The alternation is between presentation of a strong, angry invulnerable self who blames others for the problem (C1,3,5, 7) with the appearance of a fearful, weak, and vulnerable self who entices others to give succorance (C2,4,6,8). C1-2 is a very normal strategy found in people with low risk for mental health problems and a great zest for life. Infants display the C1-2 strategy.
C3-4: The C3-4 (aggressive-feigned helpless) strategy involves alternating aggression with apparent helplessness to cause others to comply out of fear of attack or assist out of fear that one cannot care for oneself. Individuals using a C3 (aggressive) strategy emphasize their anger in order to demand caregivers’ compliance. Those using the C4 (feigned helpless) give signals of incompetence and submission. The angry presentation elicits compliance and guilt in others, whereas vulnerability elicits rescue. The precursors of this strategy can be seen in infancy (using the DMM method for the Strange Situation), but the strategy only functions fully in the preschool years and thereafter.
C5-6: The C5-6 strategy (punitively obsessed with revenge and/or seductively obsessed with rescue) is a more extreme form of C3-4. It involves active deception to carry out the revenge or elicit rescue. Individuals using this strategy distort information substantially, particularly in blaming others for their predicament and heightening their own negative affect. The outcome is a more enduring and less resolvable struggle.
Those using a C5 (punitive) strategy are colder and more distant